
Smarter Wellness via IoT Health Tracking
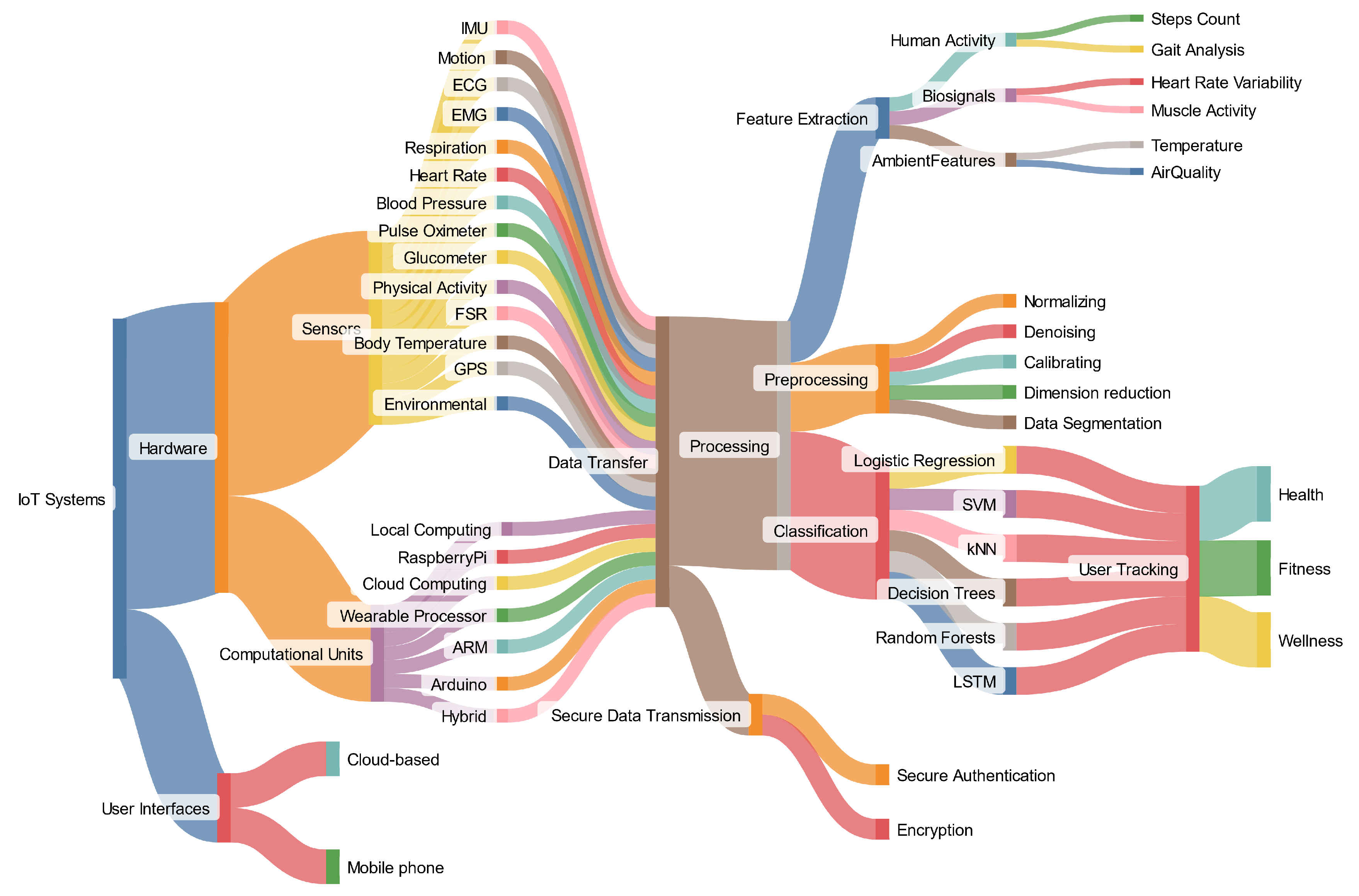
The Internet of Things (IoT) is revolutionizing the way we monitor health, fitness, and wellness. A recent systematic review published in Sensors evaluated 19 cutting-edge studies and reveals that IoT-based health tracking systems, when combined with biosensors, machine-to-machine (M2M) communication, and human-computer interaction (HCI), can provide personalized, real-time, and multimodal feedback for enhanced user wellness.
This new wave of health technologies integrates wearable sensors — such as heart rate monitors, ECG, blood pressure cuffs, and glucose trackers — with mobile apps and cloud platforms. These systems not only collect and transmit physiological data but also analyze it using artificial intelligence models like SVM, k-NN, and LSTM to detect patterns, predict health risks, and even suggest behavioral interventions.
Despite significant promise, challenges remain. Many studies suffered from small sample sizes, lacked clinical validation, or struggled with device comfort and battery limitations. Moreover, real-time operation often depended on stable internet connections, posing problems in regions with limited infrastructure. Security and privacy concerns also surfaced, highlighting the need for better encryption and user authentication.
Still, the results are compelling: over 94% accuracy in activity recognition, meaningful health outcomes like reduced HbA1c levels in diabetes patients, and high usability scores from elderly users. Future directions include integrating blockchain and federated learning for privacy-preserving analytics, enhancing edge computing for latency-free responses, and designing more ergonomic wearables.
As this research shows, IoT isn’t just about connectivity—it’s a transformative approach to preventive health and lifestyle management. By addressing existing gaps and focusing on user-centric design, IoT health systems could become essential tools for healthier, smarter living.
Adaptef from: https://www.mdpi.com/1424-8220/24/18/5939