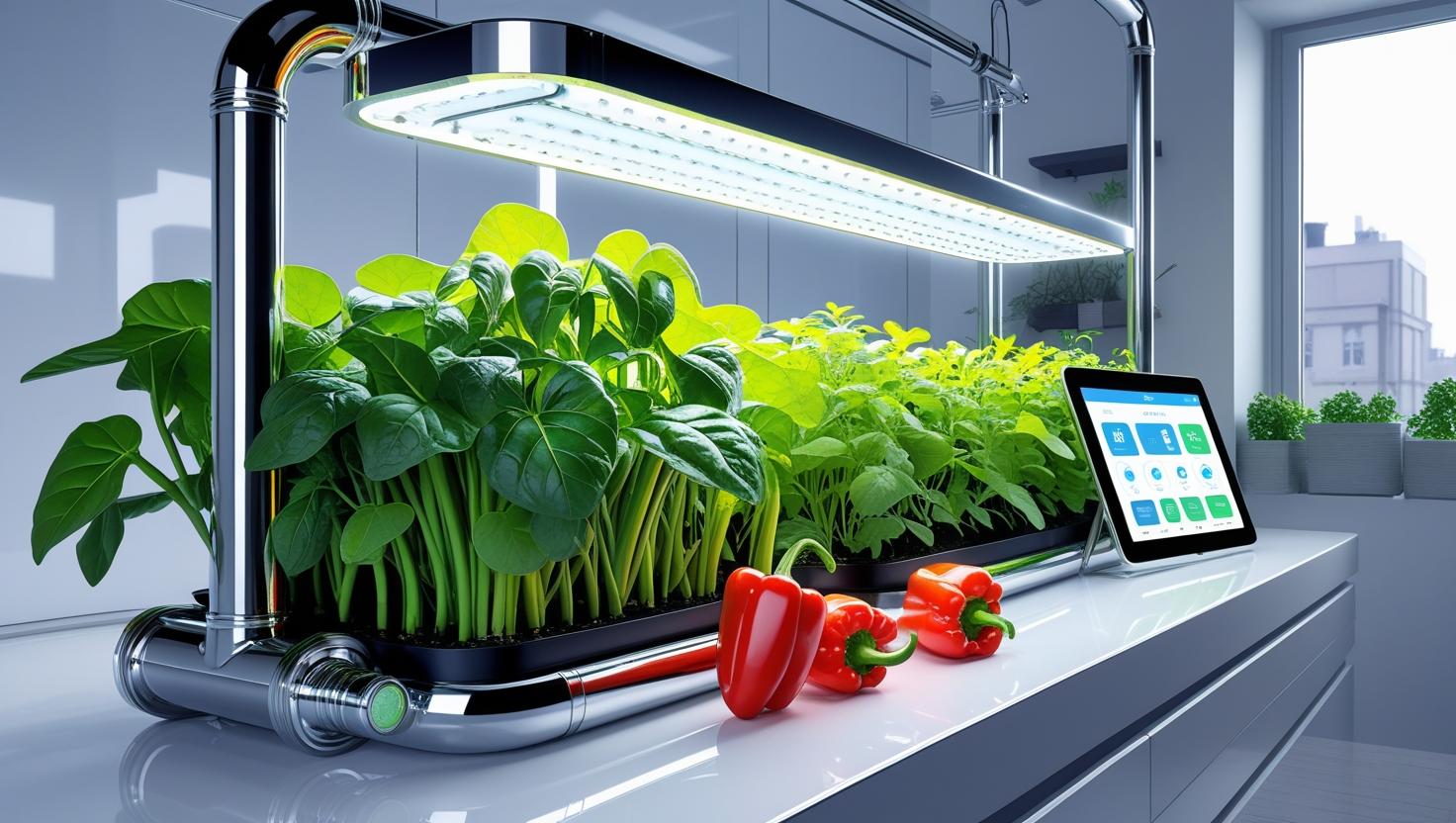

Smart Urban Farming: Home Hydroponics Future
As the global population approaches 10 billion and urbanization accelerates, traditional food systems face mounting pressure. The environmental toll of industrial agriculture—extensive land use, over-reliance on fossil fuels, excessive water consumption, and massive food waste—has become unsustainable. Addressing this challenge requires innovative, localized, and sustainable food production systems. One emerging solution is home hydroponics.
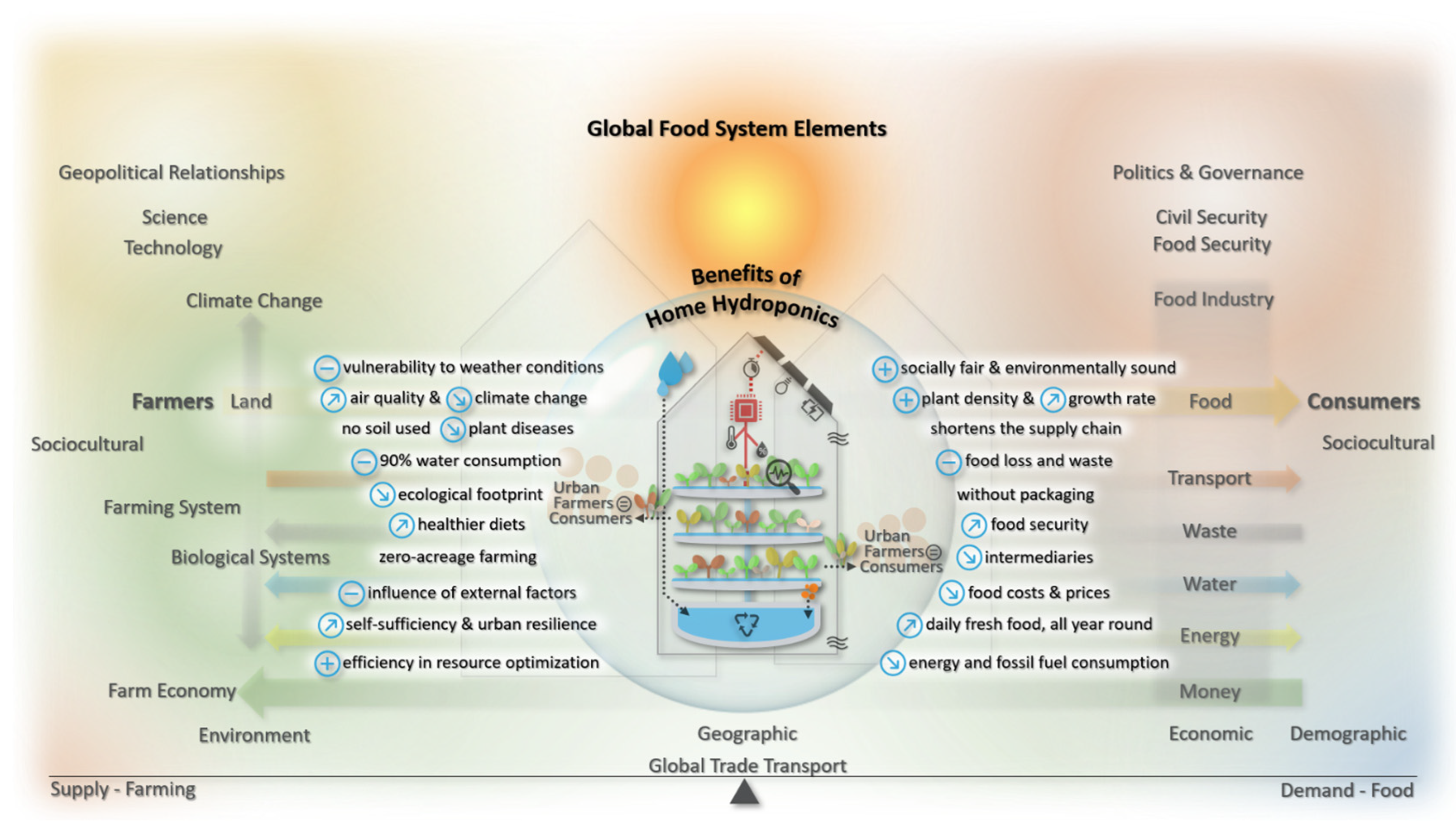
Hydroponics is a soilless method of growing plants in a nutrient-rich water solution. This technique allows for highly efficient use of space, making it ideal for urban settings like balconies, rooftops, and basements. It reduces water use by up to 90%, avoids pesticides, and produces crops 30–50% faster than soil farming.
The benefits of home hydroponics are far-reaching. It empowers citizens to grow their own vegetables, fruits, and herbs, reducing reliance on global food supply chains and promoting self-sufficiency. It cuts out middlemen, transportation emissions, and packaging waste, while delivering fresher, healthier produce. It’s a practical step toward achieving UN Sustainable Development Goal 2: Zero Hunger.
Hydroponics also aligns with the principles of circular economy. Systems can integrate waste heat, rainwater harvesting, and even organic food waste as nutrient sources. Coupled with renewable energy like solar power, hydroponics becomes a robust, climate-smart food production strategy.
Challenges remain—especially the initial cost, technical know-how, and limited crop variety—but these are steadily being addressed through smart automation and community-based initiatives.
By integrating hydroponic systems into homes and cities, we’re not just growing plants—we’re cultivating resilience, equity, and sustainability in a changing world.
Adapted from: https://www.mdpi.com/2071-1050/16/2/817